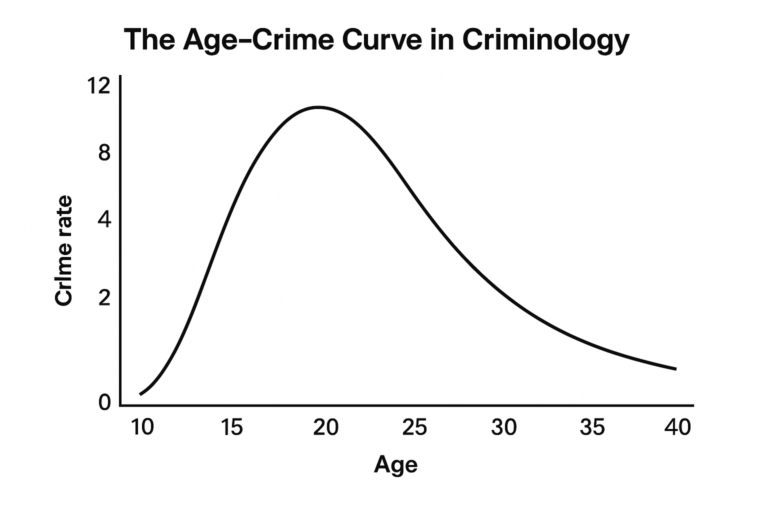
The Scientific Value of Criminal Statistics
Criminal statistics form the backbone of scientific research in criminology. These data-driven insights allow researchers, policymakers, and law enforcement agencies to understand, interpret, and respond to patterns of criminal behavior across time and space. At its core, the scientific value of criminal statistics lies in their ability to provide a systematic and objective representation of…