Criminology and Other Legal Sciences 2025
Criminology, as a multidisciplinary field, delves into understanding the causes of crime, criminal behavior, and effective methods of prevention and intervention. Its connection with other legal sciences enhances the depth and scope of criminal studies. This article explores the intricate relationships between criminology and various legal and social sciences, structured into key sections for clarity and depth.
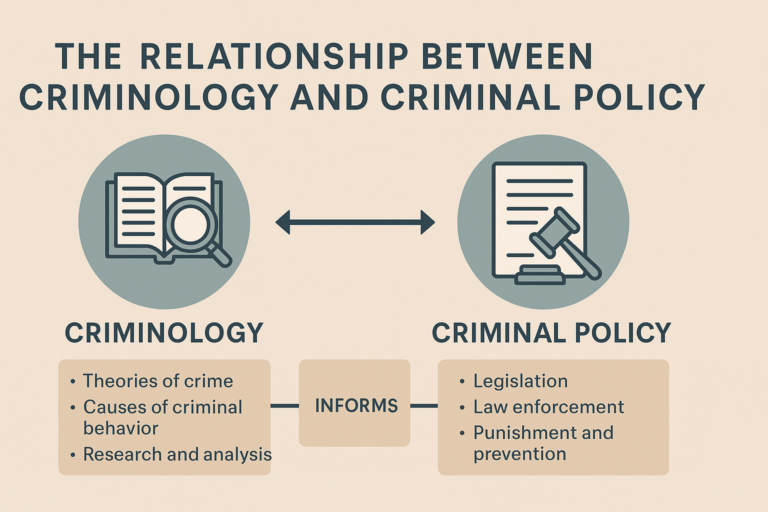
1. Criminal Policy and Criminology
Criminal policy focuses on the strategies and measures employed by governments to prevent crime and maintain public order. Criminology, on the other hand, provides the theoretical and empirical foundation necessary for shaping effective criminal policies. By studying patterns, causes, and societal impacts of crime, criminology informs policymakers on designing laws and strategies that address both prevention and rehabilitation.
For instance, criminological research has influenced modern approaches like restorative justice, which emphasizes repairing harm caused by crime rather than punitive measures alone. The synergy between these disciplines ensures that criminal policies are evidence-based and socially effective.
2. Penology and Criminology
Penology, or the study of punishment and correctional systems, is closely aligned with criminology. While criminology seeks to understand the root causes of criminal behavior, penology focuses on the appropriate responses, including incarceration, rehabilitation, and other forms of correction.
Criminological theories often guide penological practices. For example, the rehabilitation model in penology draws heavily on criminological studies that emphasize the importance of addressing social and psychological factors contributing to criminal behavior. Understanding this interplay allows for the development of humane and effective correctional systems.
3. Criminal Psychology and Criminology
Criminal psychology examines the mental and emotional processes that drive individuals to commit crimes. This branch of psychology complements criminology by providing insights into the psychological profiles of offenders, their motivations, and behavioral patterns.
Through collaboration, criminologists and criminal psychologists can develop comprehensive profiles of criminal behavior. Such profiles are instrumental in criminal investigations, risk assessments, and designing intervention programs. For example, studies on psychopathy and its correlation with criminality have advanced both fields significantly.
4. Social Criminology
Social criminology focuses on the societal factors that contribute to crime, such as poverty, inequality, and cultural norms. This branch of criminology highlights the importance of understanding crime within its broader social context.
By integrating sociological theories, social criminology provides a framework for analyzing how societal structures and interactions influence criminal behavior. This perspective is crucial for developing community-based crime prevention strategies and fostering social policies that mitigate the root causes of crime.
5. Victimology and Criminology
Victimology, the study of victims and their interactions with offenders and the criminal justice system, intersects significantly with criminology. Understanding the experiences and needs of victims helps criminologists address the full spectrum of crime—not just from the perspective of the offender but also from that of those affected by crime.
Research in victimology has led to advancements in victim support services and policies. For instance, studies on victimization patterns have informed measures to protect vulnerable populations and enhance the justice system’s responsiveness to victims’ needs.
6. Criminal Anthropology
Criminal anthropology explores the biological and physiological traits of offenders to determine potential links to criminal behavior. Historically associated with Cesare Lombroso’s work, this field has evolved to incorporate modern genetic and neurological research.
While controversial, studies in criminal anthropology have contributed to understanding how biological predispositions might interact with environmental factors to influence criminal behavior. Criminology uses these insights to develop a more holistic view of criminality.
7. Forensic Science and Criminology
Forensic science, encompassing techniques like DNA analysis, fingerprinting, and ballistic examinations, is an indispensable tool in modern criminology. By applying scientific principles to criminal investigations, forensic science enhances the accuracy and efficiency of solving crimes.
Criminologists often rely on forensic evidence to validate theories and conduct empirical studies. The integration of these fields ensures that criminological research remains grounded in practical, evidence-based findings. For instance, advancements in forensic technology have revolutionized cold case investigations and the understanding of criminal patterns.
Conclusion
Criminology’s interaction with other legal sciences enriches its capacity to address complex issues surrounding crime and justice. By collaborating with disciplines like criminal policy, penology, psychology, sociology, victimology, anthropology, and forensic science, criminology achieves a multidimensional approach to understanding and combating crime. This interdisciplinary synergy not only broadens the scope of criminological research but also enhances its application in creating safer, more equitable societies.
- Criminology
- Criminology and Law
- Criminology Studies
- Criminological Research
- Criminology Theories
- Criminal Behavior Analysis
- Criminology and Psychology
- Social Criminology
- Criminology and Forensic Science
- Victimology in Criminology
- Criminal Justice System
- Criminology and Sociology
- Penology and Criminology
- History of Criminology
- Criminology and Criminal Policy
- Criminology Fields
- Criminology and Investigation
- Applied Criminology
- Criminology Disciplines